As a business owner, you’ve poured years of effort into building your company. But do you know its true value? Whether you’re considering a sale, seeking investors, or planning for retirement, understanding how to value a business is crucial. This comprehensive guide dives into the fundamentals of business valuation, breaking down methods, calculations, and key factors that determine what your company is really worth. We’ll cover everything from basic concepts to advanced techniques, helping you avoid common pitfalls and maximize your exit potential.
Business valuation isn’t just a number—it’s a strategic tool that reveals strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities. For owners of established U.S. businesses, getting this right can mean the difference between a modest payout and a life-changing windfall. By the end of this guide, you’ll have the knowledge to assess your business accurately and decide when to seek professional help or use advanced tools.
What Is Business Valuation?
At its core, business valuation is the process of determining the economic value of a company. It involves analyzing financial statements, market conditions, assets, and future potential to arrive at a fair market price. Unlike a simple balance sheet review, valuation considers both tangible and intangible elements, providing a holistic view of your business’s worth.
Valuations are used for various purposes:
- Selling the business: To set a realistic asking price.
- Raising capital: Attracting investors or securing loans.
- Estate planning: For tax purposes or inheritance.
- Internal benchmarking: Tracking growth and performance over time.
Many owners underestimate the complexity involved. For instance, while your revenue might look impressive, buyers focus on sustainable profits and risks. If you’re wondering, “What’s Your Business Really Worth? The Owner’s Guide to Accurate Valuation (Avoid These Costly Mistakes)”, this cluster article explores the basics and highlights errors that can skew your estimate by 20-30%.
Why Should You Value Your Business Now?
Even if you’re not planning to sell immediately, valuing your business provides invaluable insights. It helps identify areas for improvement, such as boosting profitability or reducing dependencies on key personnel. According to industry data, businesses that undergo regular valuations sell for 15-25% more than those that don’t, as owners can address issues proactively.
Common triggers for valuation include:
- Exit planning: Preparing for a sale or succession.
- Growth strategies: Mergers, acquisitions, or expansions.
- Disputes: Partner buyouts or divorces.
- Financing: Demonstrating value to lenders or investors.
A shocking statistic: “Why 87% of Business Owners Overvalue Their Company (And How to Get It Right)” reveals that emotional attachment often leads to inflated expectations. This article in our cluster offers practical tips to ground your assessment in reality.
If you’re ready for a quick self-check, consider “Is Your Business Worth What You Think? Take This 60-Second Reality Check”. It’s a simple quiz that can reveal gaps in your perception versus market standards.
Common Mistakes in Business Valuation
Valuation isn’t foolproof, and errors can cost you dearly. Here are some pitfalls to avoid:
- Over-relying on revenue: High sales don’t always translate to high value if profits are thin. Dive deeper in “Revenue vs. Profit: The #1 Valuation Mistake That’s Costing You Millions”.
- Ignoring intangibles: Things like brand reputation or customer loyalty add significant value but are often overlooked.
- Using outdated data: Market conditions change; last year’s multiples may not apply today.
- DIY without expertise: While possible, amateur valuations miss nuances that professionals catch.
Another frequent error is misunderstanding earnings metrics. “EBITDA vs. SDE: Which Valuation Method Will Get You the Highest Sale Price?” compares these two key approaches, showing how SDE (Seller’s Discretionary Earnings) is ideal for small businesses, while EBITDA suits larger operations.
To steer clear of these, follow structured steps. Our cluster includes “How to Value Your Business in 5 Steps, Without Paying Thousands for an Appraiser”, a practical walkthrough for owners.
Key Business Valuation Methods Explained
There are three primary approaches to valuation: asset-based, income-based, and market-based. Each suits different business types and scenarios. Let’s break them down.
Asset-Based Valuation
This method calculates value based on your company’s assets minus liabilities. It’s straightforward for asset-heavy businesses like manufacturing or real estate.
- Book Value: Assets at historical cost. However, “Book Value vs. Market Value: Why Your Balance Sheet Lies About Your Worth” explains why this often understates true value due to depreciation.
- Liquidation Value: What assets would fetch in a quick sale—useful for distressed situations.
- Replacement Value: Cost to recreate assets from scratch.
For a deeper look, check “Asset Valuation: When Tangibles Matter More Than Cash Flow” and “Asset-Based vs. Income-Based Valuation: Which Method Maximizes Your Exit Price?”.
Income-Based Valuation
Focused on future earnings potential, this is popular for service-based or high-growth companies.
- Capitalization of Earnings: Divides normalized earnings by a capitalization rate. Learn more in “Normalized Earnings: How to Present Your True Profit Potential to Buyers”.
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF): Projects future cash flows and discounts them to present value. “Discounted Cash Flow Made Simple: Value Your Business Like a Wall Street Pro” simplifies this, while “Terminal Value in DCF: How Future Assumptions Impact Today’s Asking Price” covers long-term projections. Key components include the “Weighted Average Cost of Capital: The Discount Rate That Defines Your Worth”.
- Seller’s Discretionary Earnings (SDE): Adjusts for owner perks. “SDE Valuation Demystified: Calculate Your Seller’s Discretionary Earnings in 5 Minutes” provides a quick calculator guide. Explore the fundamentals of SDE in this guide from Corporate Finance Institute.
Also, explore “How to Calculate Adjusted EBITDA: Add-Backs That Legitimately Increase Your Value” for EBITDA tweaks that boost perceived value.
For a comprehensive overview of EBITDA, refer to this Investopedia article.
Market-Based Valuation
Compares your business to similar sold companies.
- Comparable Company Analysis: Uses multiples from peers. “Market Comparables: Finding Similar Sales That Justify Your Asking Price” guides you on sourcing data.
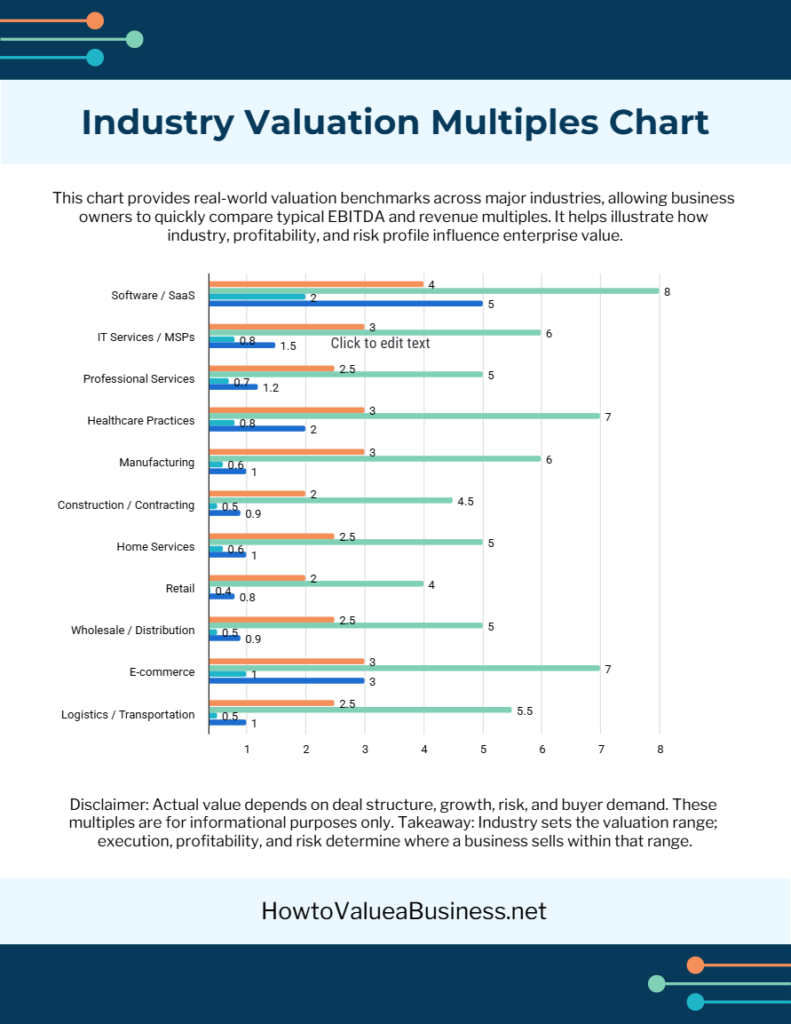
- Industry Multiples: Applies benchmarks like 3-5x EBITDA. “Business Valuation Multiples by Industry: Where Does Your Company Really Stand?” and “What Buyers Actually Pay: Industry Multiples That Determine Your Exit Value” offer sector-specific insights. Beware the “The Rule of Thumb Trap: Why Industry Standards Often Mislead Sellers”.
- The Multiple Method: “The Multiple Method: How to Apply Industry Benchmarks to Your Financials” and “The 3x, 4x, 5x Rule: What Multiple Should You Really Expect?” detail application.
For an overview of all methods, see “How Much Is My Business Worth? 5 Proven Methods to Calculate Your True Value”.

Factors That Influence Your Business Valuation
Beyond methods, several elements can swing your value by 10-50%.
- Financial Health: Steady revenue growth and strong margins are key. “Revenue Multiples Are Lying to You: Why Smart Sellers Focus on Profit Instead” shifts focus to earnings.
- Market Conditions: Economic trends, industry demand, and competition.
- Operational Risks: Customer concentration, supply chain issues, or key person dependencies.
- Intangibles: “Goodwill and Intangibles: Capturing the Hidden Value Buyers Actually Pay For” covers patents, brands, and relationships.
- Working Capital: “Working Capital Adjustments: The Closing-Day Calculation That Changes Your Payout” explains post-sale tweaks.
- Hidden Factors: “The Hidden Factors That Make or Break Your Business Valuation (Buyers Won’t Tell You This)” reveals buyer perspectives.
- Enterprise Value (EV): “Enterprise Value Explained: What Business Owners Get Wrong About EV” clarifies this debt-inclusive metric.
Industry plays a huge role, specialty tech firms might fetch 10x revenue, while retail averages 2-4x EBITDA.
Step-by-Step Guide to Valuing Your Business
Ready to try it yourself? Here’s a streamlined process:
- Gather Financials: Collect 3-5 years of statements, including adjustments for non-recurring items.
- Choose Methods: Select 2-3 based on your business type (e.g., DCF for growth-oriented).
- Apply Calculations: Use tools or formulas—start with SDE or multiples.
- Adjust for Factors: Factor in risks and intangibles.
- Validate: Compare against comparables and seek feedback.
For detailed steps, refer to our cluster articles like “Discounted Cash Flow Analysis: When to Use This Premium Valuation Method”.
Free vs. Professional Valuation: What’s Right for You?
Many owners start with free online calculators or templates, which provide a ballpark figure. However, for accuracy, professionals like appraisers or brokers are essential, especially for sales.
- DIY Pros: Cost-effective, quick. Tools can handle basic SDE or multiples.
- Cons: Misses nuances, potential bias.
- When to Hire: Complex businesses, high stakes, or legal needs.
Explore “Free vs. Professional Valuation – When to DIY and When to Hire an Expert” for guidance.
Taking the Next Step: Maximize Your Business Value
Valuing your business is the first step toward unlocking its full potential. Armed with these fundamentals, you can make informed decisions that drive growth or prepare for a successful exit. But theory only goes so far, real insights come from personalized analysis.
If you’re ready to go beyond basics, explore our related articles for deeper dives. Or, for actionable results, try our AI-powered tools that deliver custom valuations, readiness assessments, and enhancement roadmaps tailored to your business.
Don’t leave your company’s worth to guesswork. Start today and discover what buyers see in your enterprise.
